Chromophilia
20 January – 9 March 2022
Zurich, Limmatstrasse
‘The obvious thing to say is that colour speaks for itself in art, and that any attempt to speak on its behalf is bound to fail. And yet for all the small talk that might happily be silenced forever, there is at the same time a bigger silence around the very subject of colour in art...’—David Batchelor, Chromophobia (2000)

Explore the exhibition
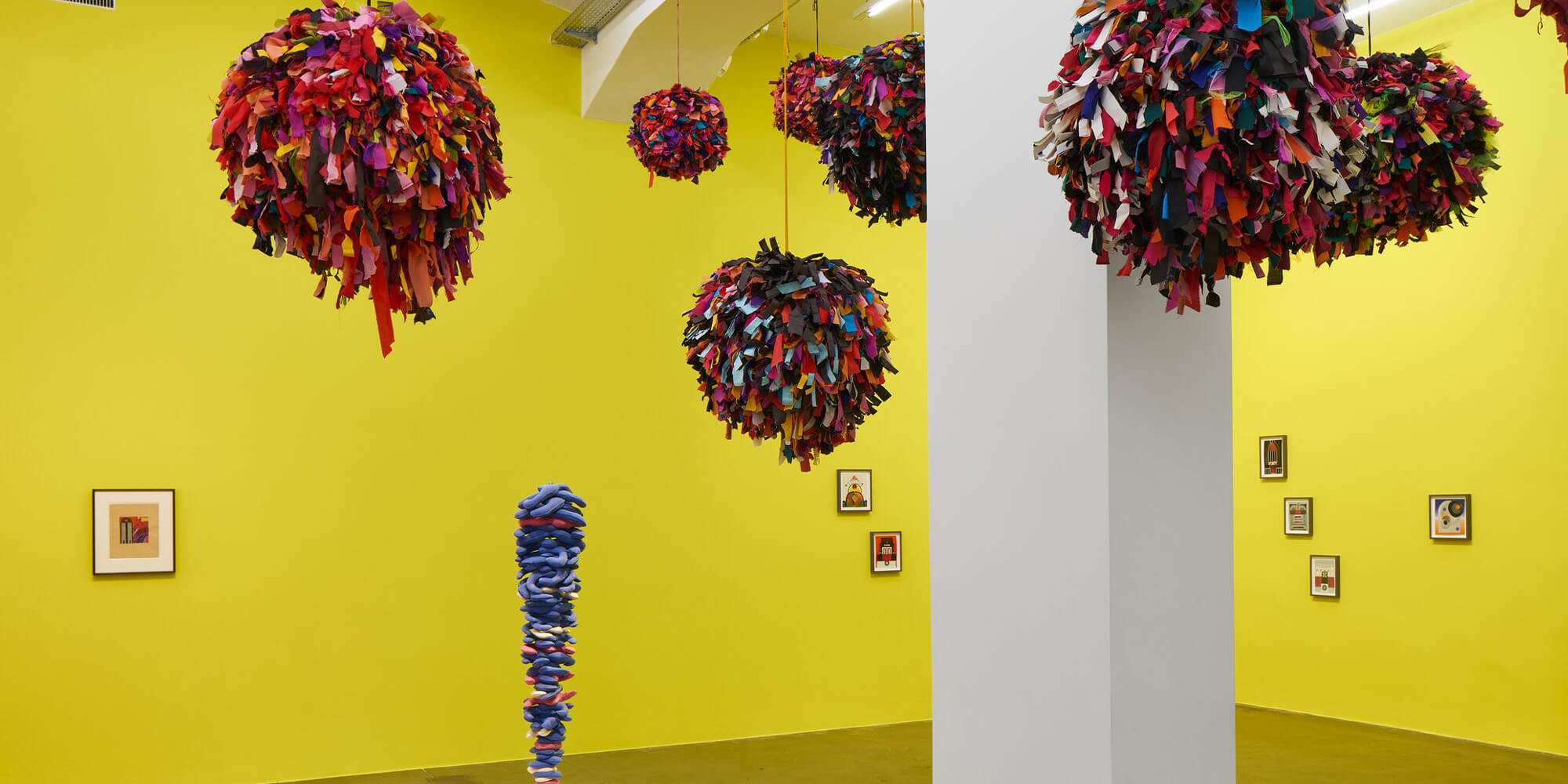
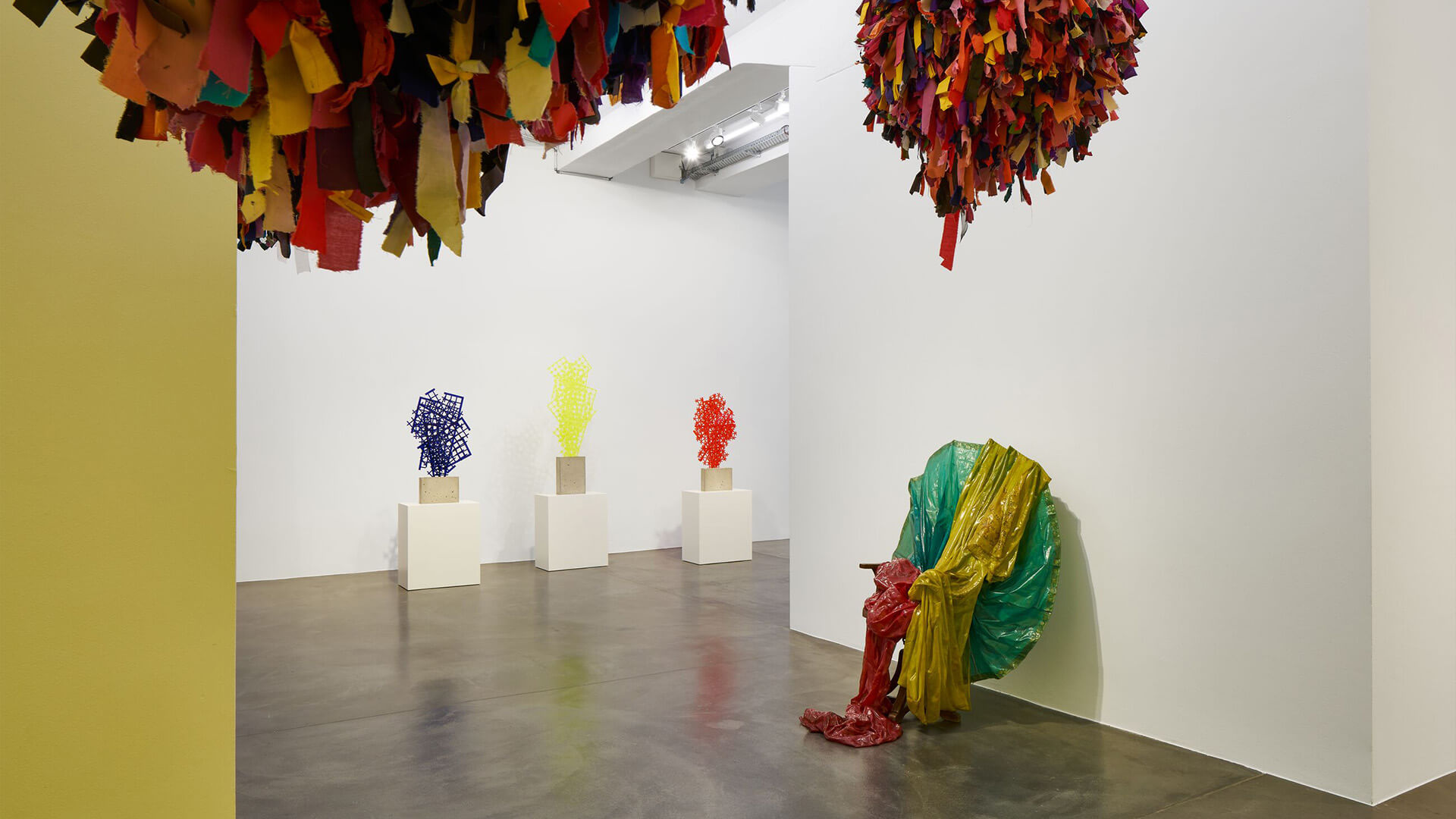
Colour is not a simple subject. In this group exhibition, titled ‘Chromophilia’ meaning the love of colour, the artists on view trace the complexity and possibility of colour, emancipated to differing degrees from line and form, within their chosen medium either synthetic or found – from liquid paint to sewn fabric, from coloured glass to LEDs, from neon to bindis.
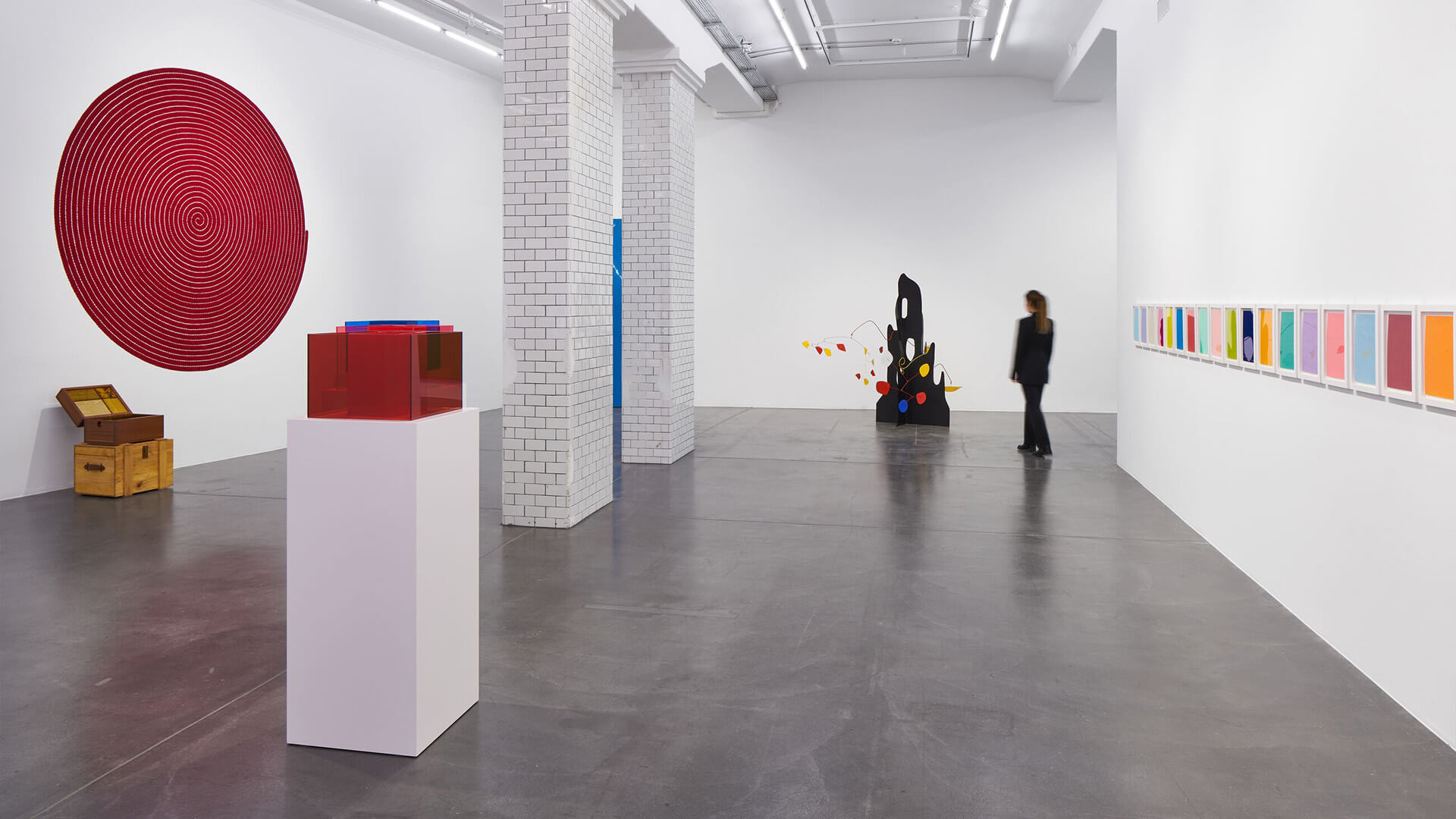

‘Chromophilia’ brings together paintings, collages, sculptures and installations by artists including Phyllida Barlow, David Batchelor, Larry Bell, Louise Bourgeois, Frank Bowling, Geta Brătescu, Alexander Calder, Martin Creed, Günther Förg, Mary Heilmann, Jenny Holzer, Roni Horn, Bharti Kher, Yves Klein, John McCracken, Jason Rhoades, Pipilotti Rist, Sophie Taeuber-Arp and Elisabeth Wild.

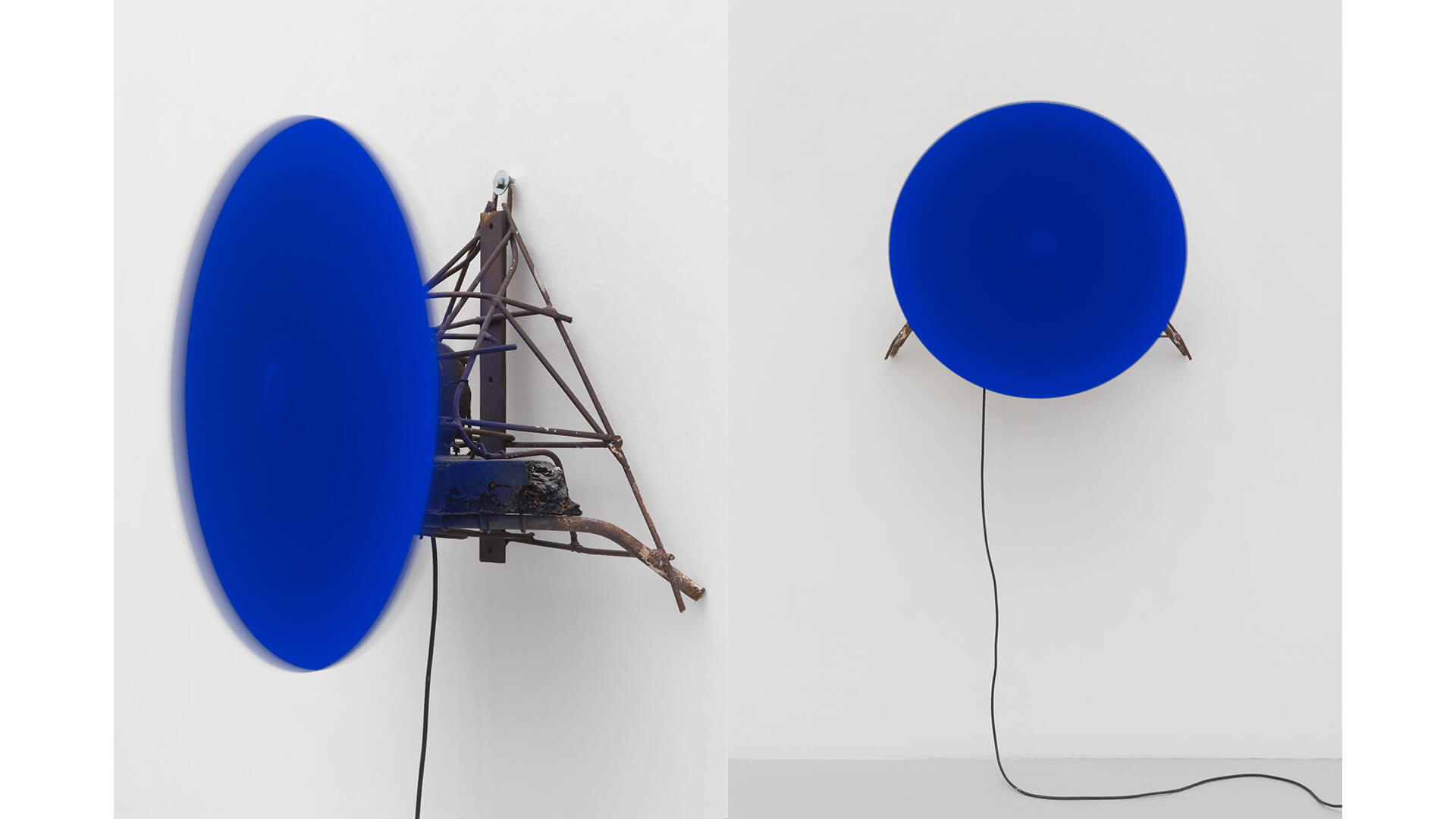
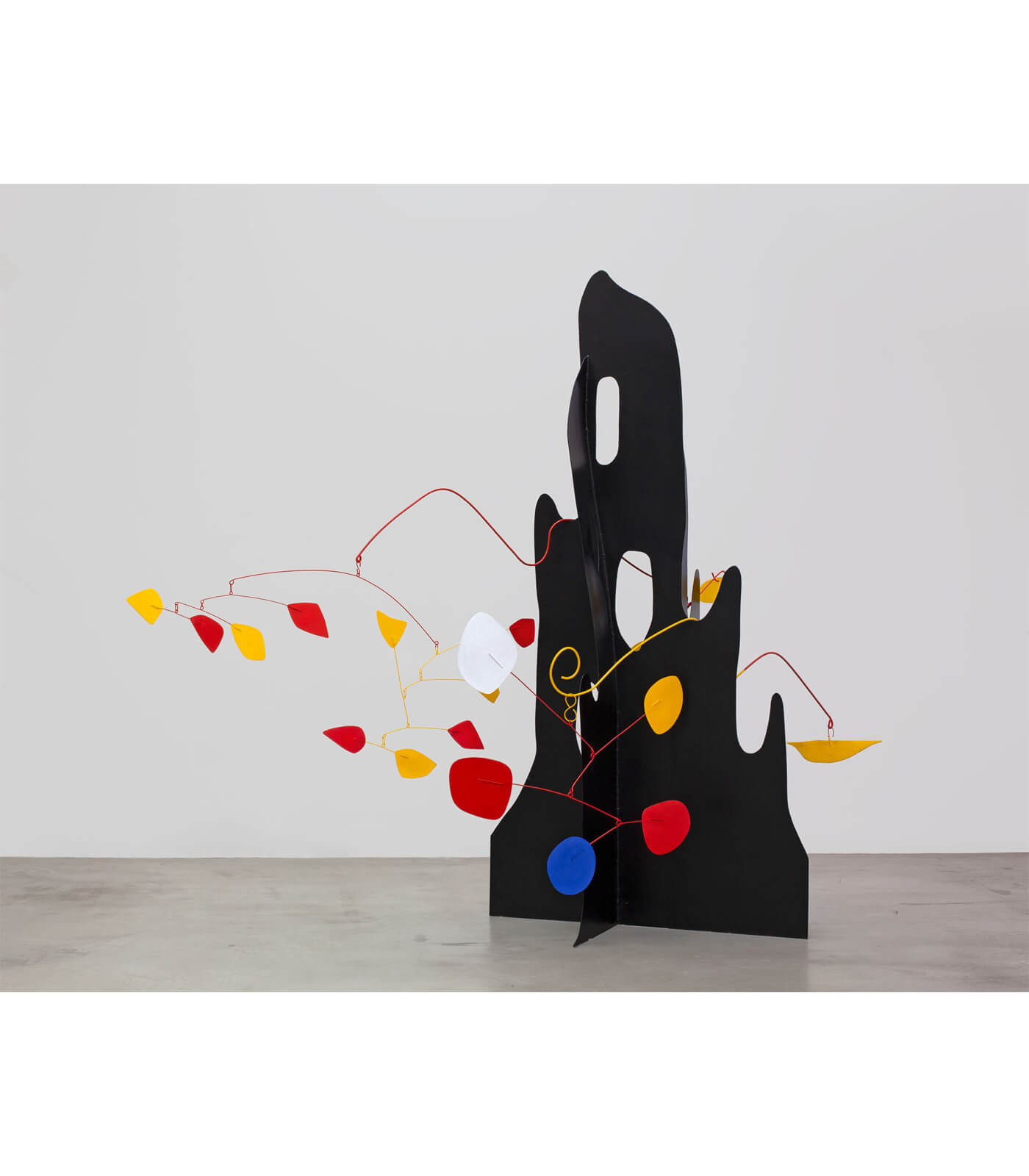
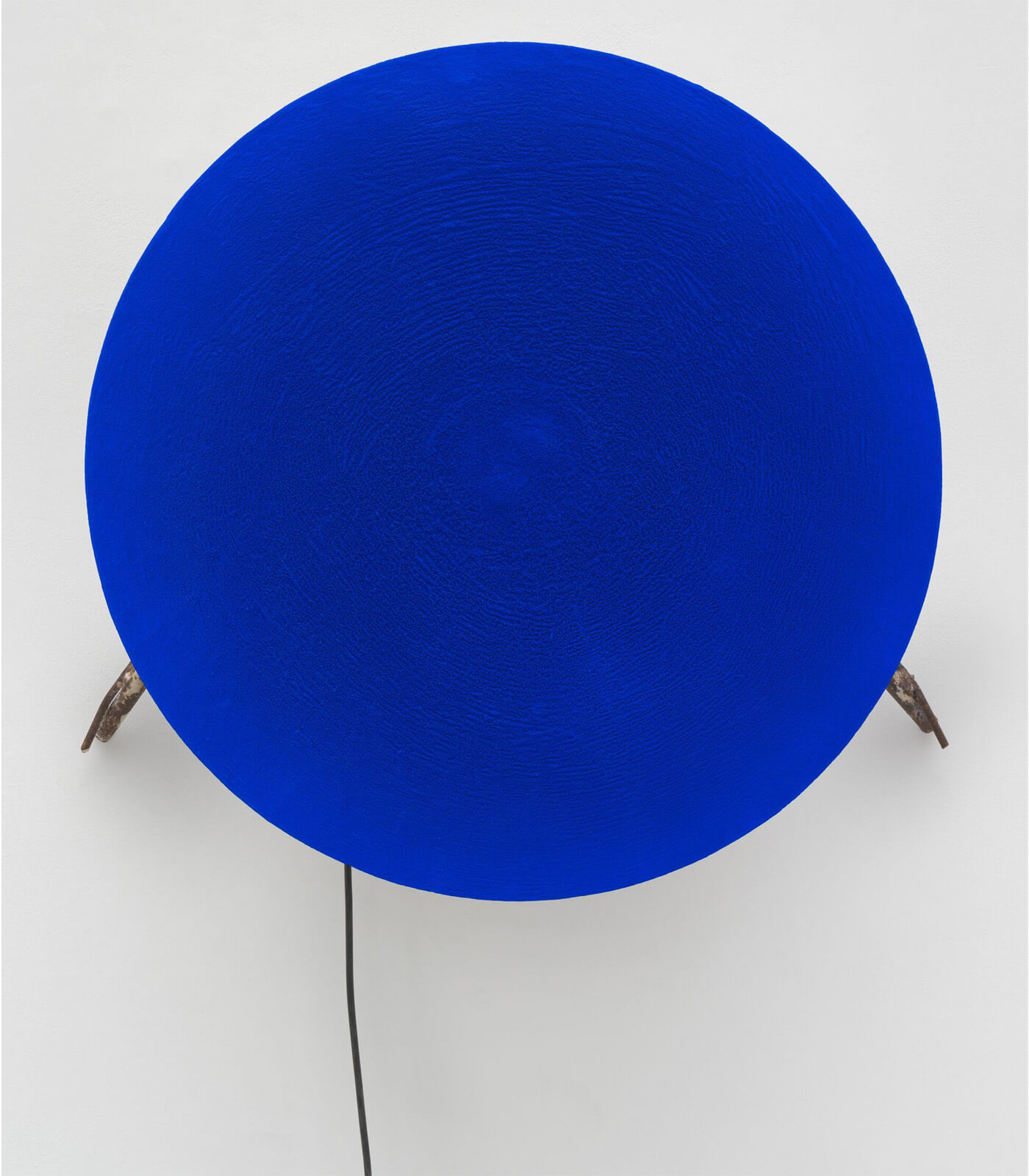
Until the 20th Century, colour in European, or Western, art was largely subordinated to line and form. The emancipation of colour in modern art came with the advent of movements such as impressionism, pointillism, fauvism, or the aptly named Blue Rider, and with the early development of modernist abstraction. The role of colour changed radically with the work of pioneering artists from Hilma af Klint to Hélio Oiticica, and with Yves Klein, whose work ‘Total Speed (Crazed Blue)’ 1958, a collaboration with Jean Tinguely, is on view in the exhibition.
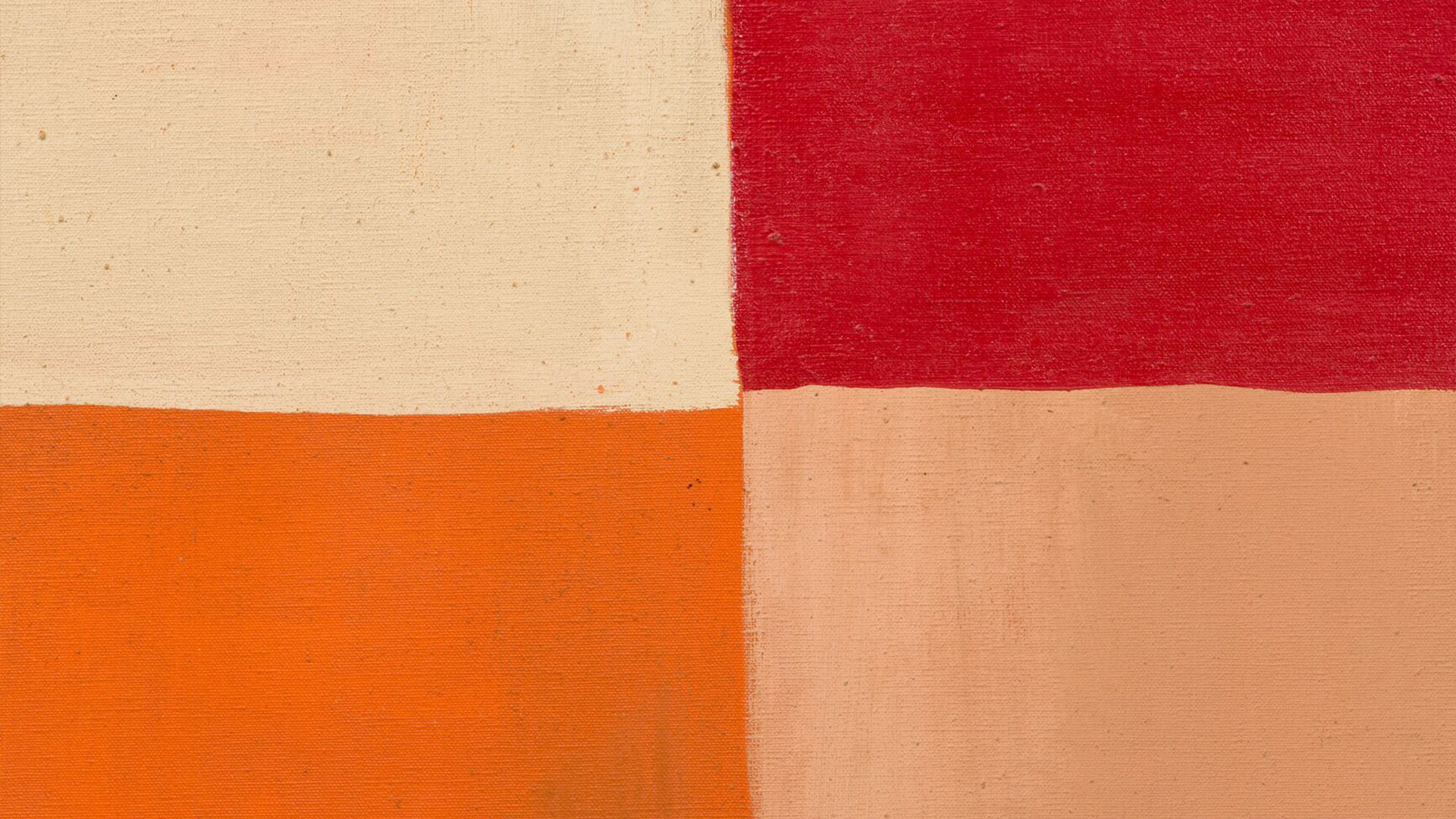

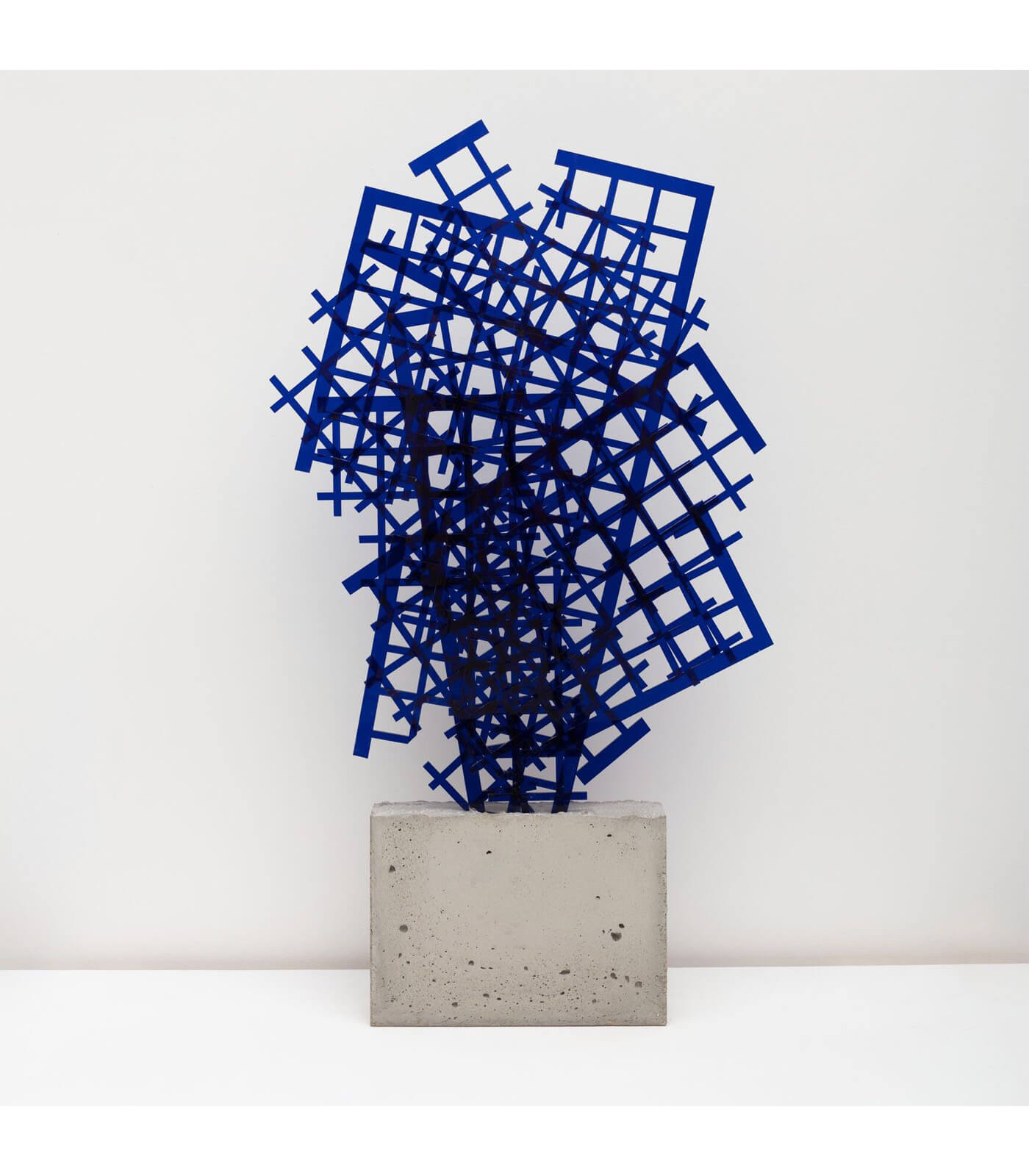
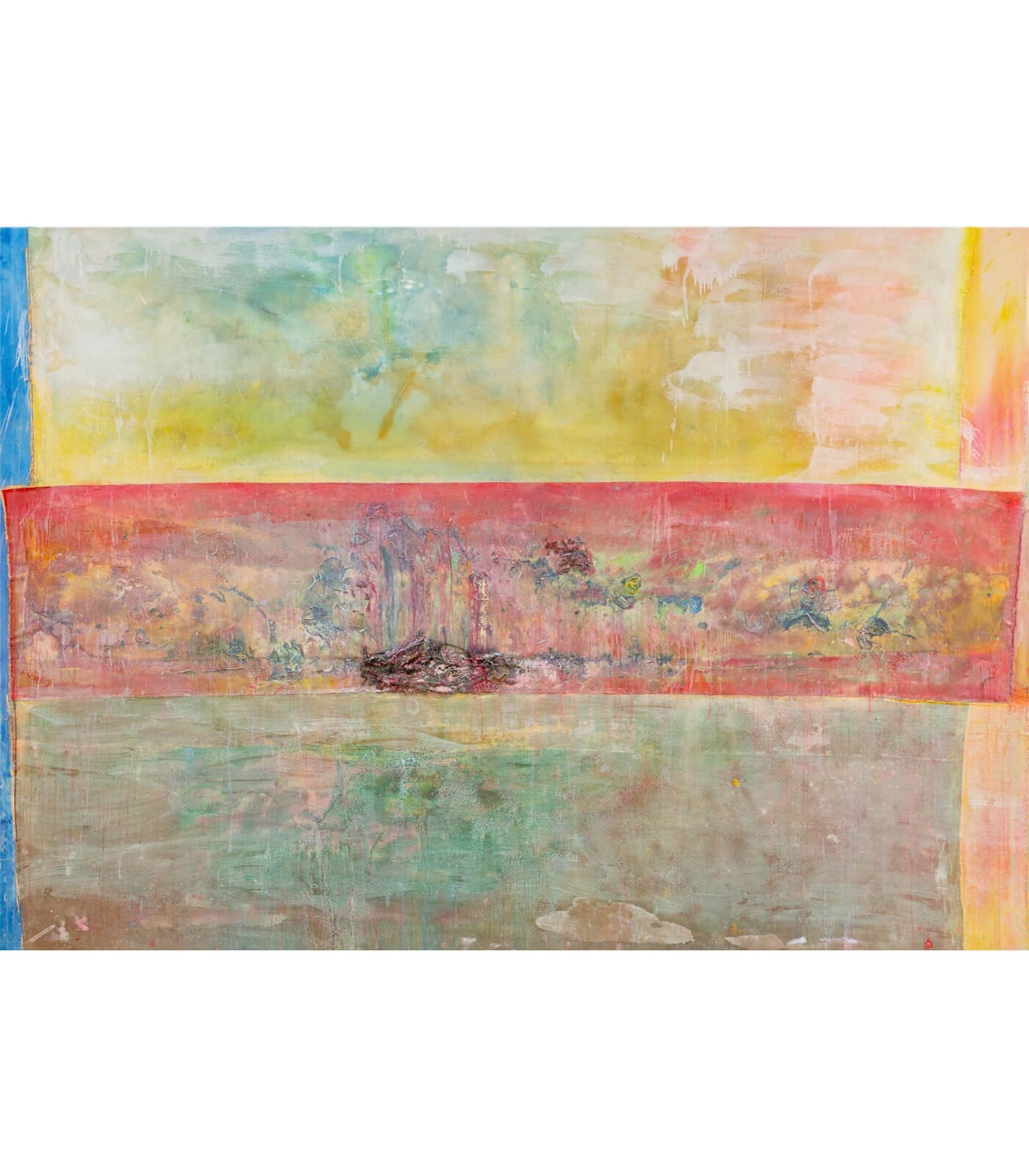
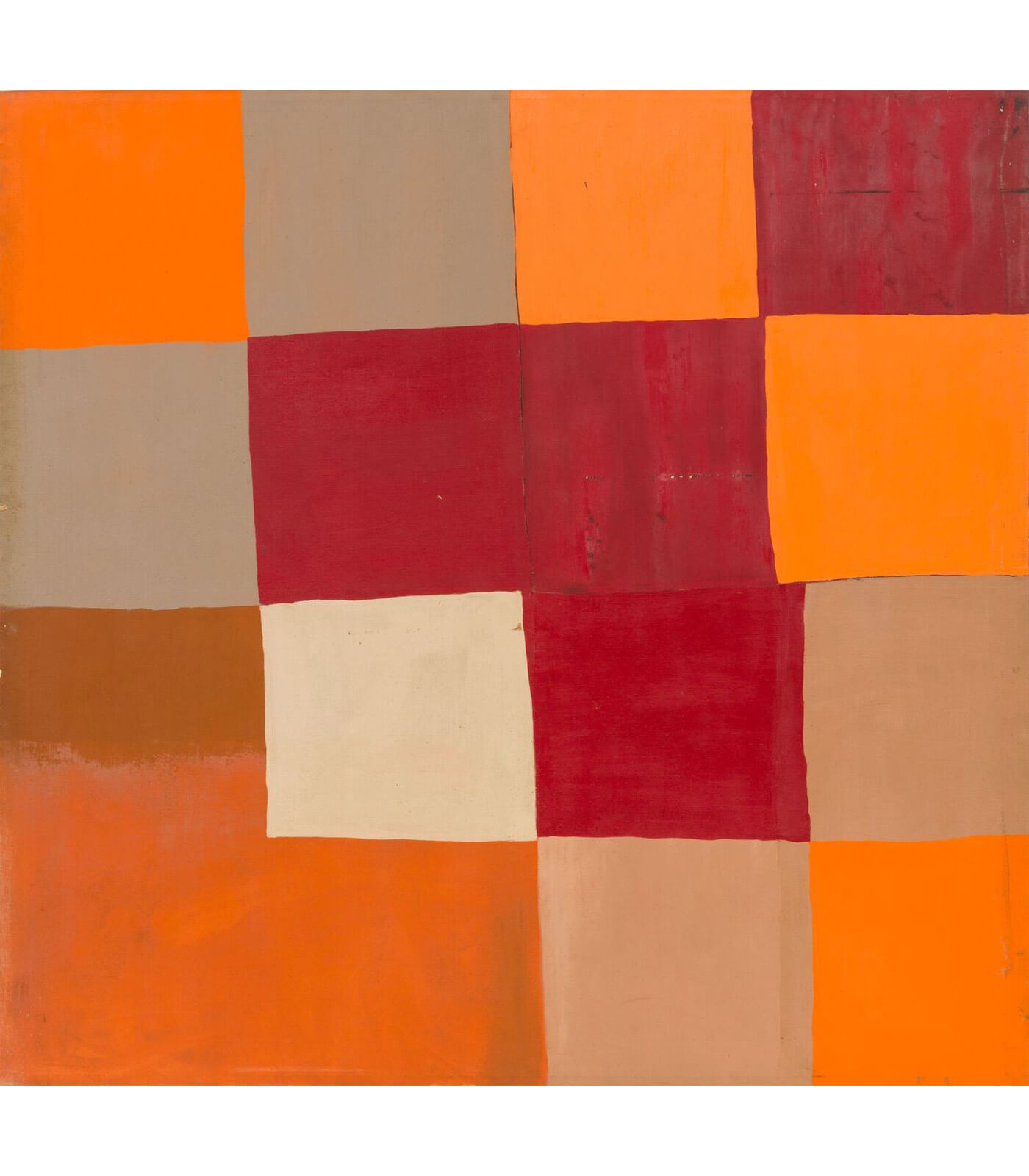
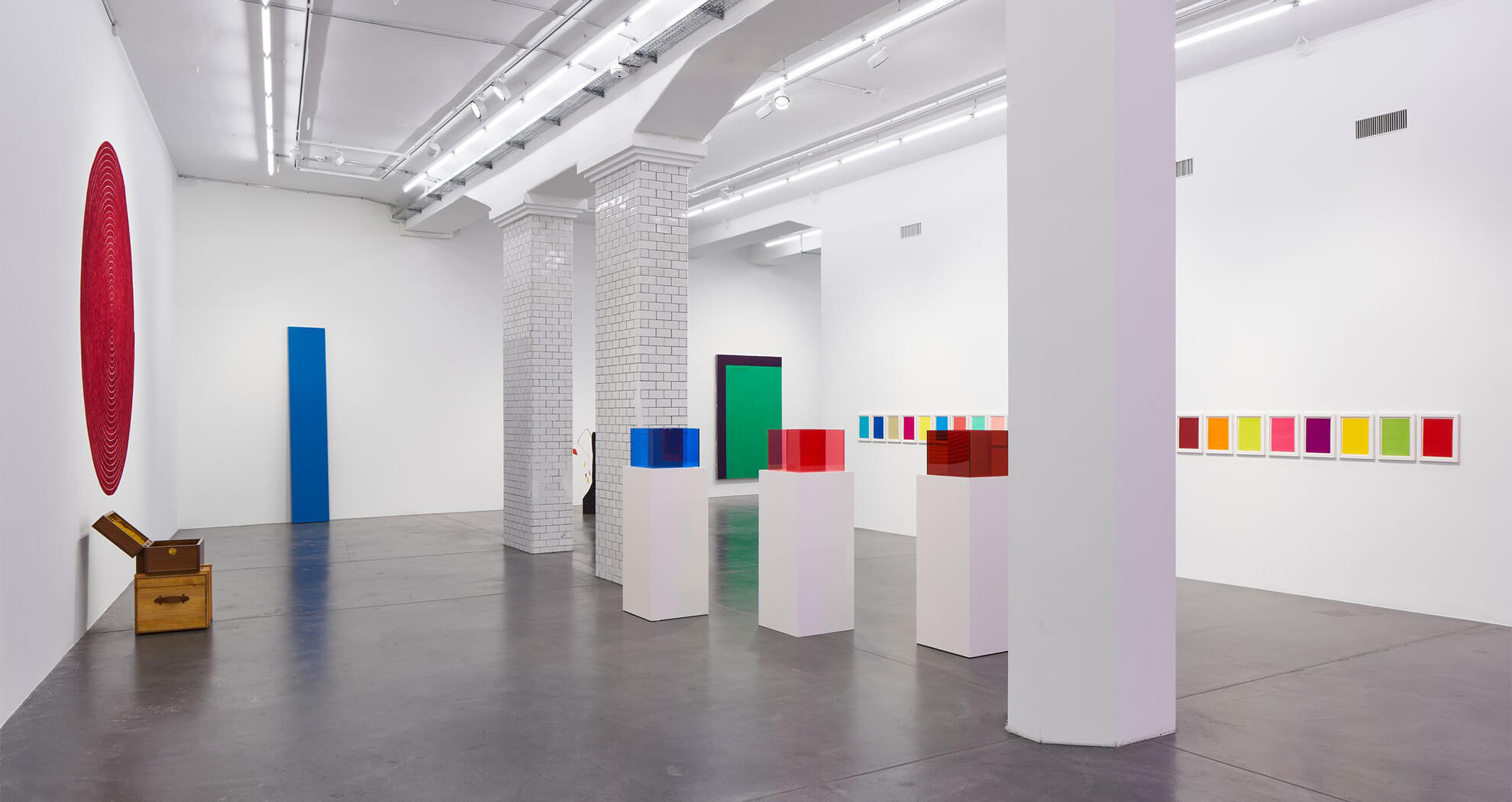
A concentration on colour remains a complex topic and the radical, though deceptive, simplicity of the use of single colours, particularly as monochromes, has been one of its most challenging aspects. Extending beyond the monochrome to explore close colour contrasts, Larry Bell’s early oil on canvas ‘Untitled’ (1959) ranges from orange and taupe to sienna and wine. This work anticipates his vibrantly tinted glass sculptures, such as ‘Pacific Red (IV)’ (2016-2017). Both show him to be a formidable colourist.
Colour has the capacity to work in myriad ways, representing opposing psychological states, from exuberant joy to crushing despair. Like music, brilliant colour can lift our spirits or stimulate memory; and artists have often turned to synaesthesia to develop their work.
Colour, however, can be and frequently is highly symbolic, and often it is politicised, representing partisan ideologies, playing a role in activism or denoting race and gender. Colour is not impartial and white is also a colour, not necessarily or merely its absence. Colour is historically defined and located; it changes according to its given cultural associations. In the short, dark days of winter we embrace intense and magnificent colour in festivals and celebrations that serve to reinforce identity.
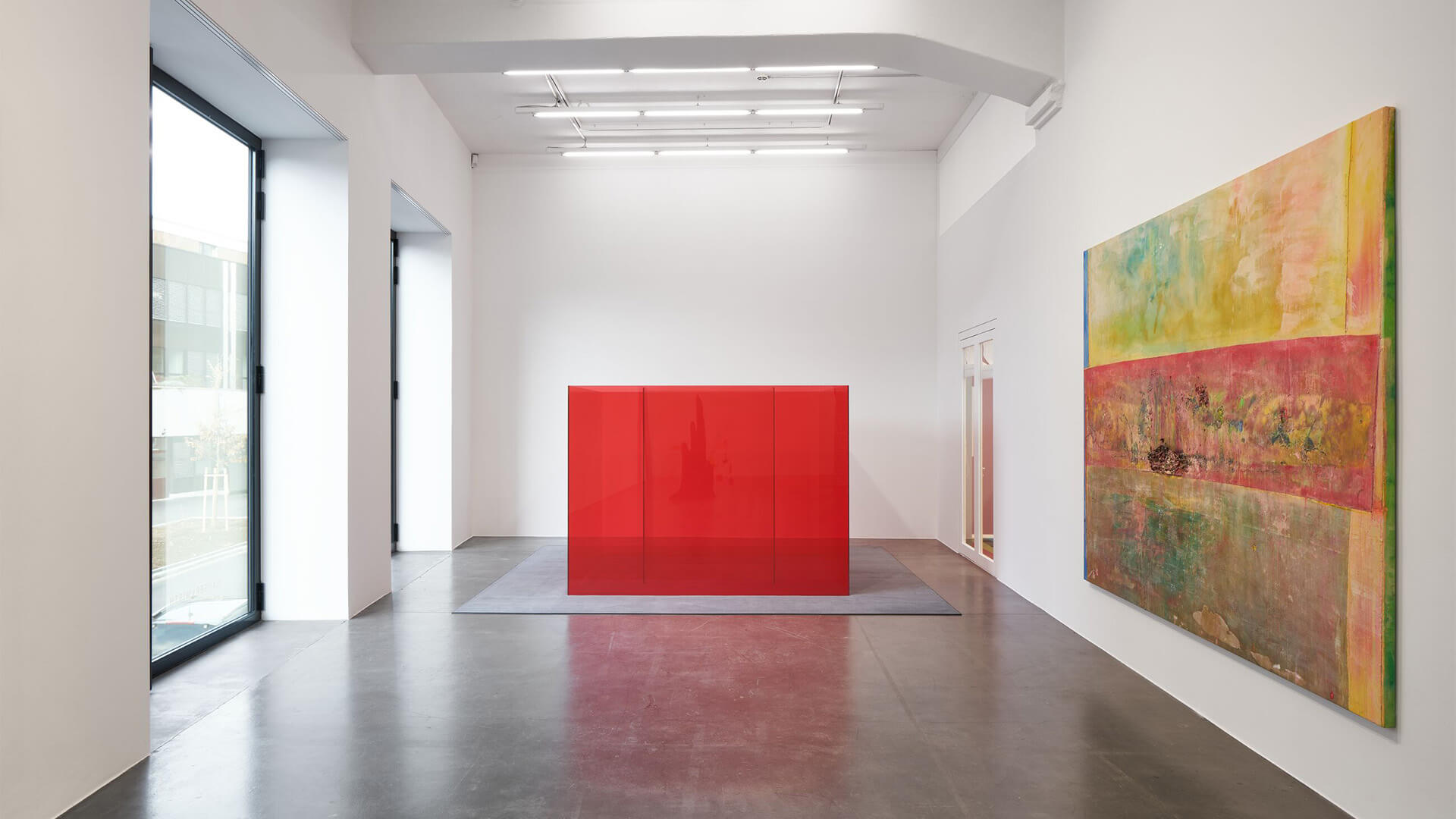

Throughout his career Frank Bowling has engaged with the complexity of colour in painting, and has developed his own highly original approaches to chromatic abstraction. His work ‘Swimmers’ (2020) presents the viewer with a dense, layered surface, composed from acrylic paints and gels, collaged canvas and found materials or objects.
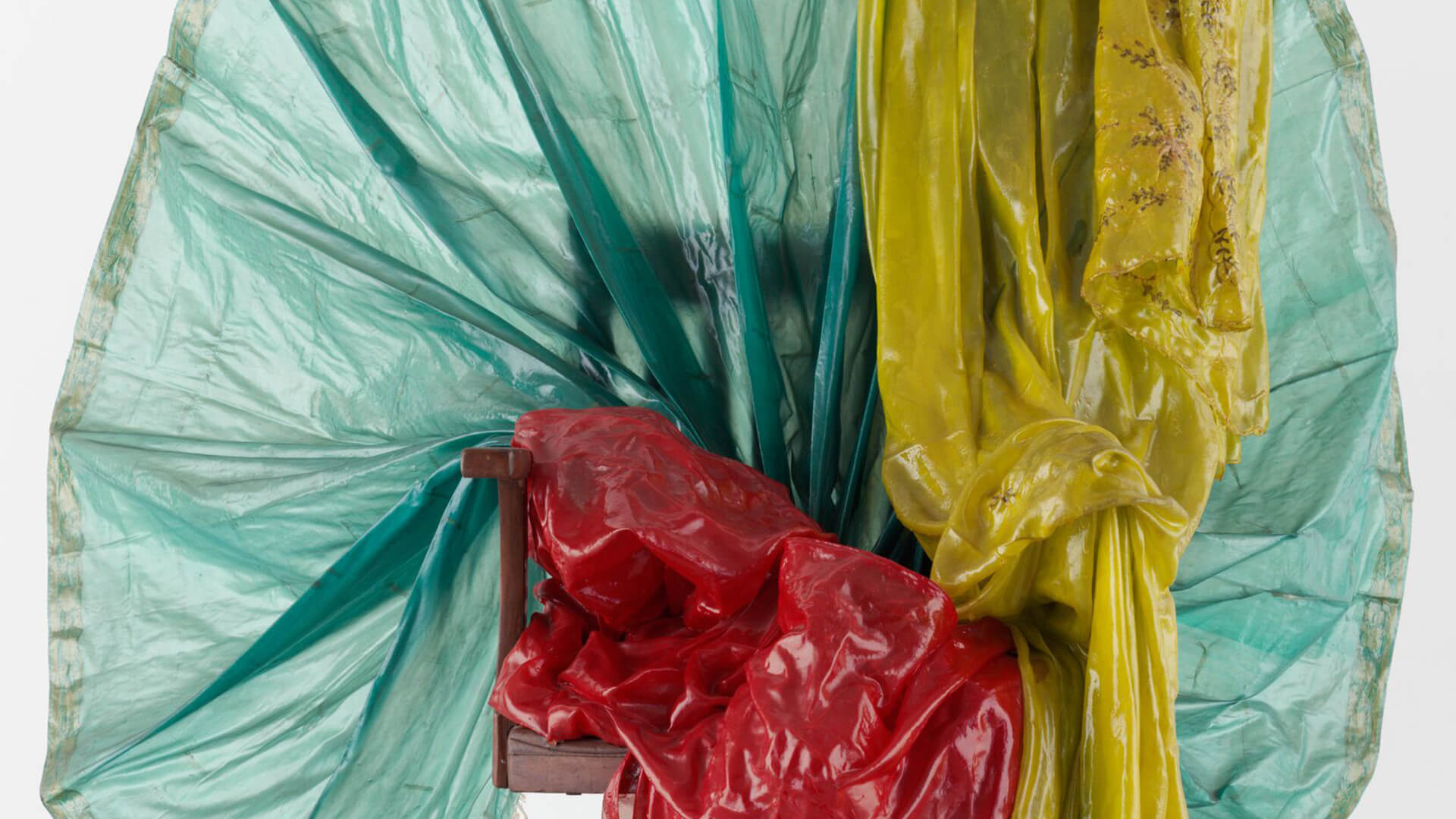

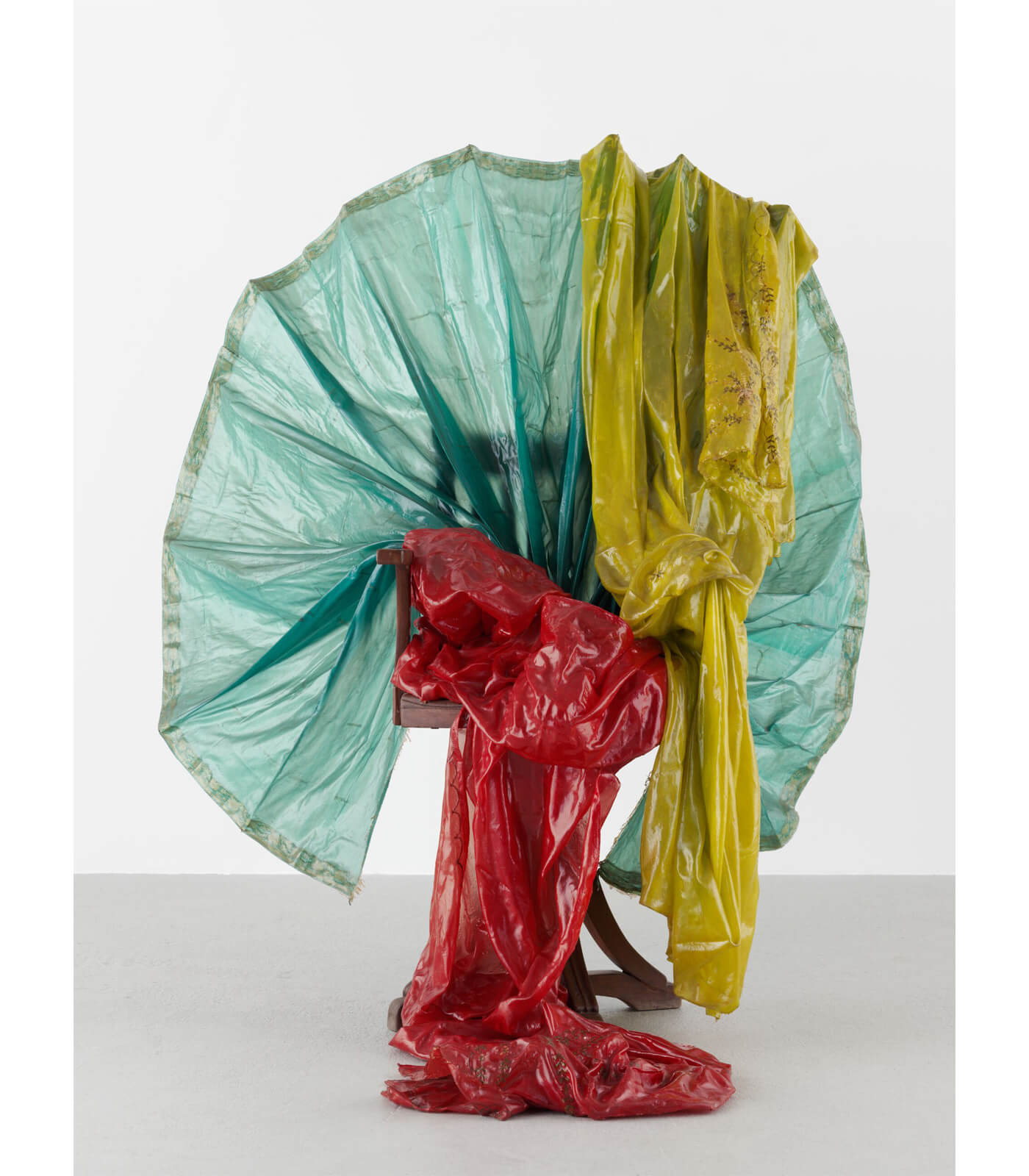
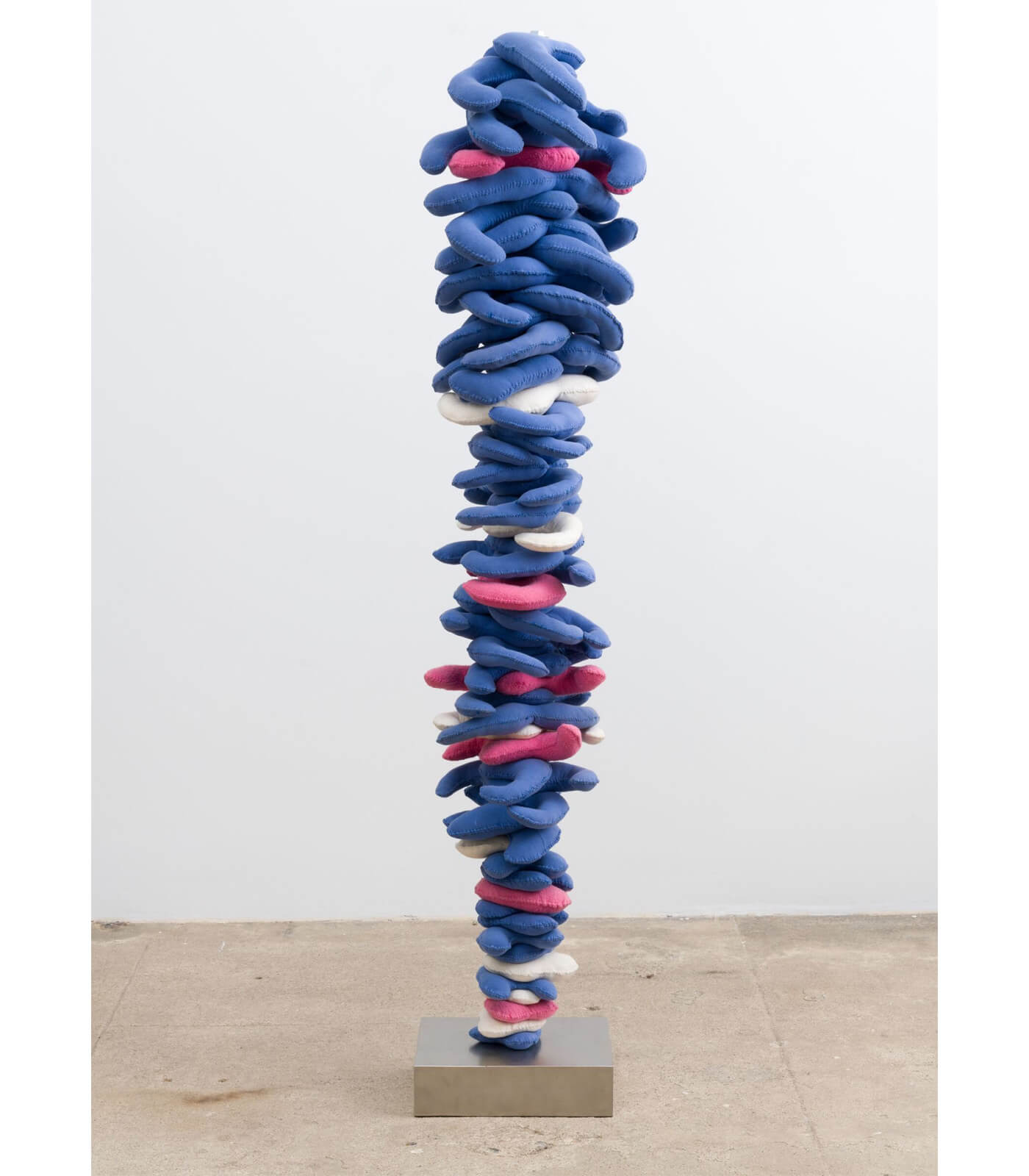
Bharti Kher’s sculpture ‘Peacock’ (2011) employs sari fabrics dipped in resin; by forming the bright green, shimmery blue and regal red fabrics into a peacock-like shape, Kher draws our attention to the transformation of everyday materials, likewise to the relation of colour to the body, and also to the important roles colour plays in India.
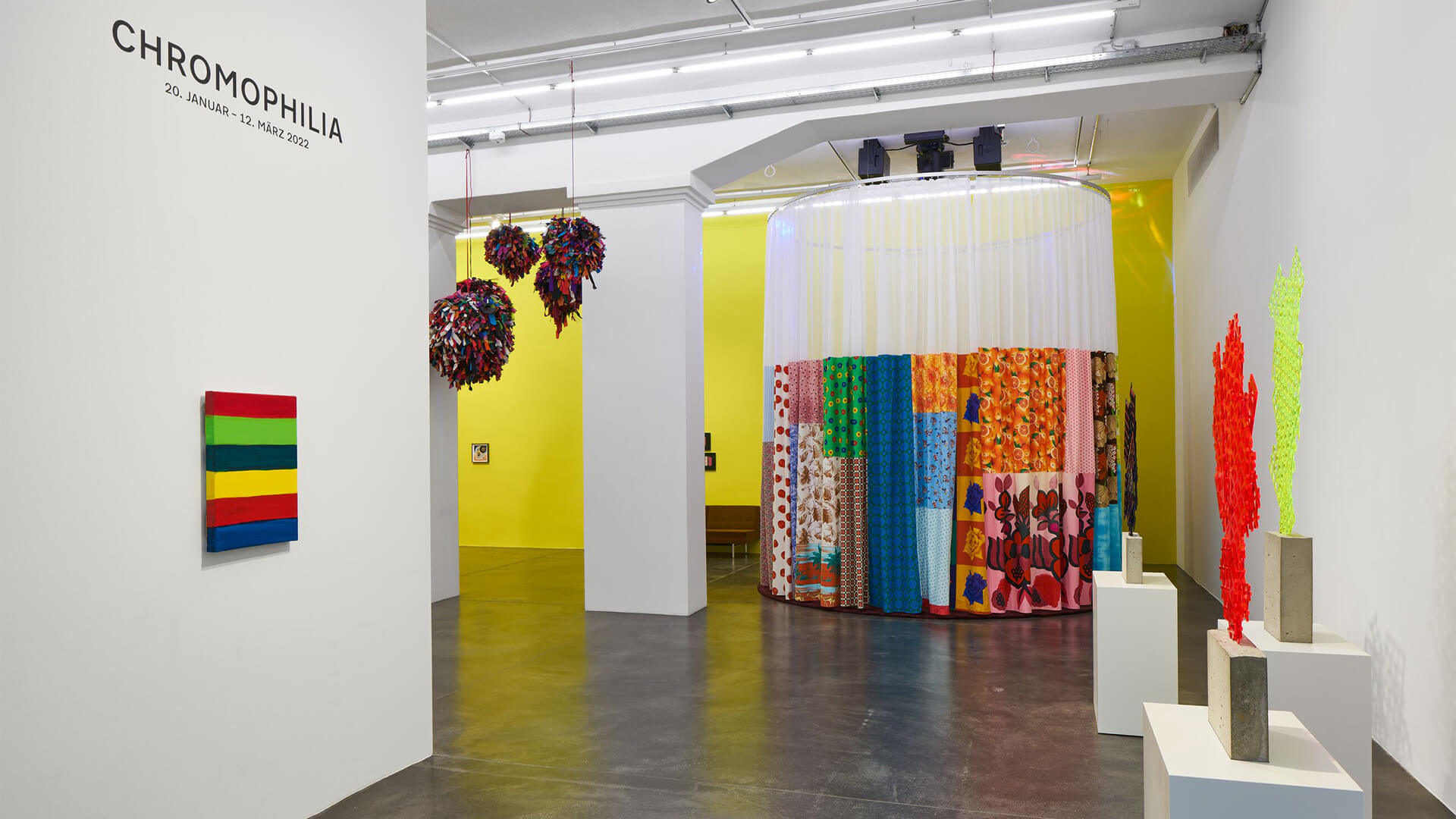

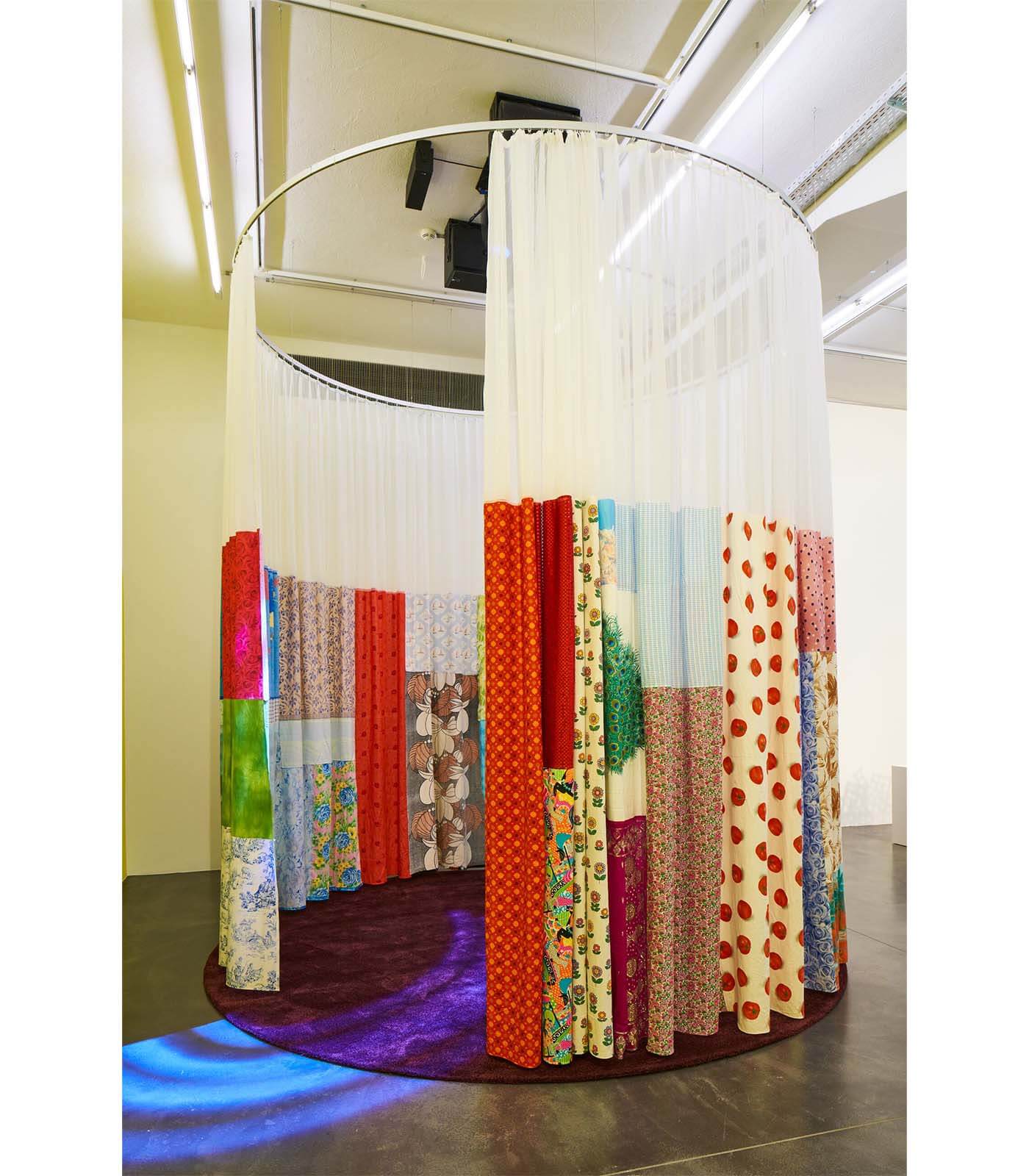
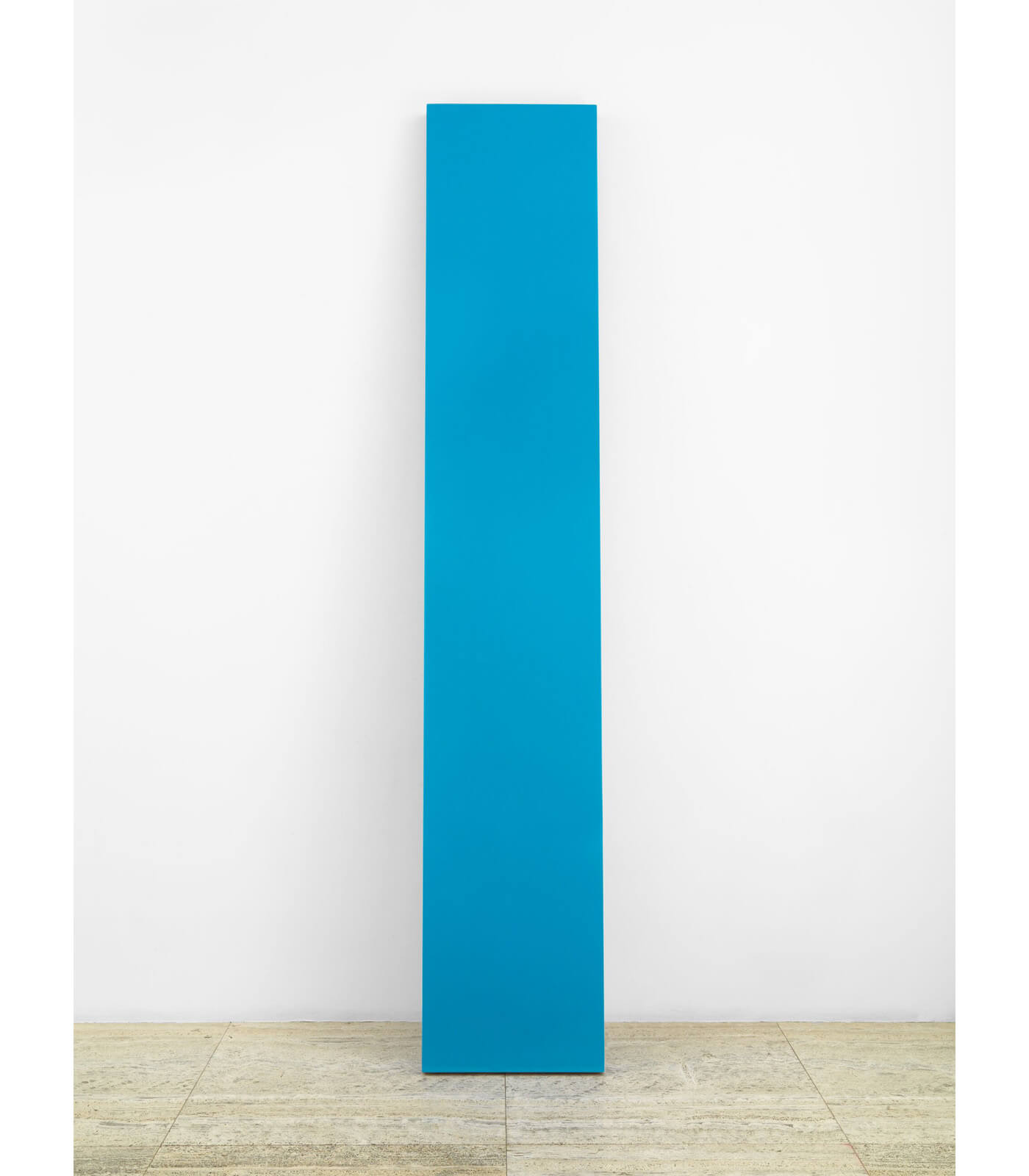
Occupying the full height of the exhibition space, Pipilotti Rist’s immersive installation ‘Wohnzimmerdisco ohne Angst (Living Room Disco without Fear)’ (2009) combines carpets and curtains, with sound and light to create a shower of vivid colour tones. David Batchelor’s ‘Chromodisc’ (2019) is a sculptural clock that uses light to move through the colour spectrum over the course of an hour. Overall, the artists included in ‘Chromophilia’ deploy colour always in inventive and extraordinary ways, helping us to see and experience our world anew.

On View in Zurich, Limmatstrasse
‘Chromophilia’ is on view now through 9 March 2022 at Hauser & Wirth Zurich, Limmatstrasse.
About the Artists

Roni Horn
Roni Horn’s work consistently generates uncertainty to thwart closure in her work. Important across her oeuvre is her longstanding interest to the protean nature of identity, meaning, and perception, as well as the notion of doubling; issues which continue to propel Horn’s practice.
Since the mid-1990s, Horn has been producing cast-glass sculptures. For these works, colored molten glass assumes the shape and qualities of a mold as it gradually anneals over several months. The sides and bottom of the resulting sculpture are left with the rough translucent impression of the mold in which it was cast. By stark contrast, the top surface is fire-polished and slightly bows like liquid under tension. The seductively glossy surface invites the viewer to gaze into the optically pristine interior of the sculpture, as if looking down on a body of water through an aqueous oculus. Exposed to the reflections from the sun or to the shadows of an overcast day, Horn’s glass sculpture relies upon natural elements like the weather to manifest her binary experimentations in color, weight and lightness, solidity and fluidity. The endless subtle shifts in the work’s appearance place it in an eternal state of mutability, as it refuses a fixed visual identity. Begetting solidity and singularity, the changing appearance of her sculptures is where one discovers meaning and connects her work to the concept of identity.
For Horn, drawing is a primary activity that underpins her wider practice. Her intricate works on paper examine recurring themes of interpretation, mirroring and textual play, which coalesce to explore the materiality of color and the sculptural potential of drawing. Horn’s preoccupation with language also permeates these works; her scattered words read as a stream of consciousness spiralling across the paper. In her ‘Hack Wit’ series, Horn reconfigures idiomatic turns of phrase and proverbs to engender nonsensical, jumbled expressions. The themes of pairing and mirroring emerge as she intertwines not only the phrases themselves but also the paper they are inscribed on, so that her process reflects the content of the drawings. Words are her images and she paints them expressionistically, which—combined with her method—causes letters to appear indeterminate, as if they are being viewed underwater.
Notions of identity and mutability are also explored within Horn’s photography, which tends to consist of multiple pieces and installed as a surround which unfolds within the gallery space. Examples include her series ‘The Selected Gifts, (1974 - 2015),’ photographed with a deceptively affectless approach that belies sentimental value. Here, Horn’s collected treasures float against pristine white backdrops in the artist’s signature serial style, telling a story of the self as mediated through both objects and others—what the artist calls ‘a vicarious self-portrait.’ This series, alongside her other photographic projects, build upon her explorations into the effects of multiplicity on perception and memory, and the implications of repetition and doubling, which remain central to her work.

Mary Heilmann
Influenced by 1960s counterculture, the free speech movement, and the surf ethos of her native California, Mary Heilmann ranks amongst the most influential abstract painters of her generation. Considered one of the preeminent contemporary Abstract painters, Heilmann’s practice overlays the analytical geometries of Minimalism with the spontaneous ethos of the Beat Generation, and are always distinguishable by their often unorthodox—always joyful—approach to color and form.
Raised in San Francisco and Los Angeles, Heilmann completed a degree in literature, before she studied ceramics at Berkeley. Only after moving to New York in 1968 did she begin to paint. While most artists at that time were experimenting with the concept of dematerialization and demanding that painting should avoid any references to experience outside the material presence of the work itself, Heilmann opted for painting, rebelling against the accepted rules. ‘Rather than following the decrees of modern, non-representational formalism, I started to understand that the essential decisions taken during the creative process were more and more related to content. The Modern movement was over…’
Since then, Heilmann has created compositions that evoke a variety of associations. Her work may be non-representational and based on an elementary, geometrical vocabulary—circles, squares, grids and stripes—but there is always something slightly eccentric, casual about them. The simplicity of the forms is played down by a deceptive form of nonchalance: the contours are not clearly defined. In some paintings, amorphous forms appear to melt into each other like liquid wax. Splashes of color can be discerned, sharp edges bleed for no apparent reason, and the ductus of the brushstrokes is always perceptible. Heilmann’s casual painting technique conceals a frequently complex structure that only gradually reveals itself to the viewer.
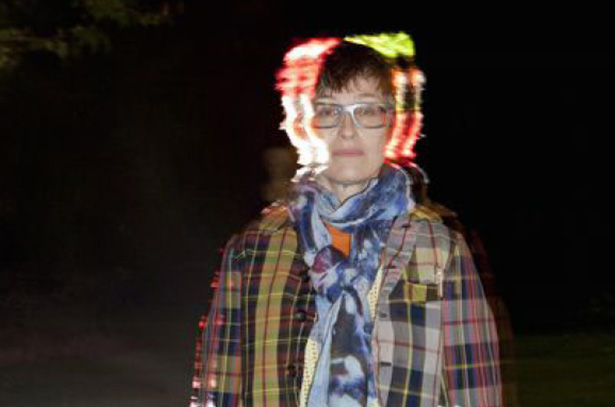

Pipilotti Rist
Pipilotti Rist, a pioneer of spatial video art, was born 1962 in Grabs in the Swiss Rhine Valley on the Austrian Border and has been a central figure within the international art scene since the mid-1980s.
Astounding the art world with the energetic exorcistic statement of her now famous single channel videos, such as ‘I’m Not The Girl Who Misses Much,’ 1986 and ‘Pickelporno,’ 1992, her artistic work has co-developed with technical advancements and in playful exploration of its new possibilities to propose footage resembling a collective brain. Through large video projections and digital manipulation, she has developed immersive installations that draw life from slow caressing showers of vivid color tones, like her works ‘Sip My Ocean,’ 1996 or ‘Worry Will Vanish,’ 2014.
For Rist, showing vulnerability is a sign of strength on which she draws for inspiration. With her curious and lavish recordings of nature (to which humans belong as an animal), and her investigative editing, Rist seeks to justify the privileged position we are born with, simply by being human. Her installations and exhibition concepts are expansive, finding within the mind, senses and body the possibility for endless discovery and poetical invention. ‘Pixel Forest,’ 2016, made from 3,000 thousand LEDs hung on strings, resembles a movie screen that has exploded into the room, allowing viewers an immersive walk through 3-dimensional video. As she herself puts it, ‘beside the energy-intensive exploration of the geographical world, pictures, films and sounds have been and are the spaces into which we can escape... The projector is the flamethrower, the space is the vortex and you are the pearl within.’
Since 1984, Rist has had countless solo and group exhibitions, and video screenings worldwide. Her recent solo exhibitions are 'Electric Idyll' at the Fire Station Doha (2024), 'Prickling Goosebumps & A Humming Horizon' at Hauser & Wirth New York and Luhring Augustine Chelsea (2023-24), 'Behind Your Eyelid' at Tai Kwun Hong Kong (2022), ‘Big Heartedness, Be My Neighbor’ at The Geffen Contemporary, MOCA, Museum of Contemporary Art Los Angeles (2021 – 2022), ‘Your Eye Is My Island’ at MoMAK, The National Museum of Modern Art Kyoto and ART TOWER MITO (2021). ‘Åbn min Lysning. Open my Glade’ at Louisiana Museum of Modern Art Humlebæk Denmark (2019), ‘Sip My Ocean’ at the Museum of Contemporary Art Sydney (2017 – 2018), ‘Pixel Forest’ at New Museum New York (2016 – 2017) and ‘Your Saliva is My Diving Suit of the Ocean of Pain’ at Kunsthaus Zürich (2016), all resulted in record-breaking attendance numbers for each institution. A major exhibition is planned for summer 2025 at UCCA Beijing.
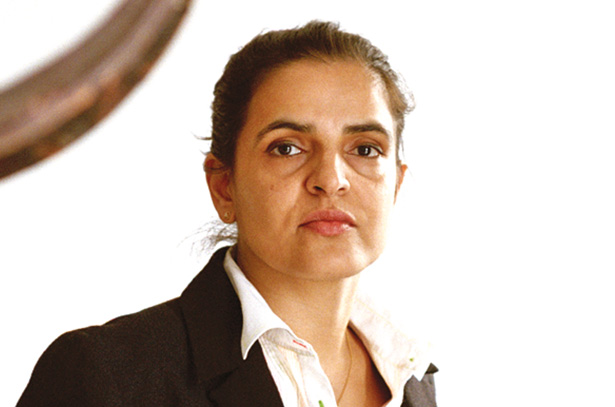

Bharti Kher
Born in London in 1969, Bharti Kher’s art gives form to quotidian life and its daily rituals in a way that reassesses and transforms their meaning to yield an air of magical realism. Now living between London, UK and New Delhi, India, her use of found objects is informed by her own position as an artist located between geographic and social milieus. Her way of working is exploratory: surveying, looking, collecting, and transforming, as she repositions the viewer’s relationship with the object and initiates a dialogue between metaphysical and material pursuits.
The bindi is an iconic personal affect of Indian women that is one of Kher’s signature materials and a loaded symbol. Since first appearing in her work in 1995, the bindi has inherited an aesthetic and cultural duality, a means to mix the superficial with the sublime. Kher explains: ‘Many people believe it’s a traditional symbol of marriage while others, in the West particularly, see it as a fashion accessory... But actually the bindi is meant to represent a third eye—one that forges a link between the real and the spiritual-conceptual worlds.’ Used as a material to articulate and animate her themes, bindis as such are not meant to be the central-motif of her work but rather act as a material, much like paint or clay, but with an inherent narrative. The bindis themselves undergo a shift in their initial cultural capital—they are defamiliarized, made to seem both scientific and mystical.
At the center of Kher’s practice are her sculptures, early examples of which featured fantastical hybrid characters, blurring the distinctions between humans and nature, ecology and politics. In line with this early practice, Kher continues to assemble, juxtapose and transform found objects that are witness to their own histories. Wooden wheels and architectural remnants, mannequin body casts and pillars all clash in mis-en-scenes of dystopia and grand orchestration. These elements are assembled in a hazardous manner; suspended from the ceiling, hanging from ropes, propped up and held from falling with the help of counterweights and balances; ultimately forming a heterogeneous narrative in which Kher further explores the artistic strategy of stripping objects of their meaning and making them open to misinterpretation and magic, creating alluring works of abstract beauty.
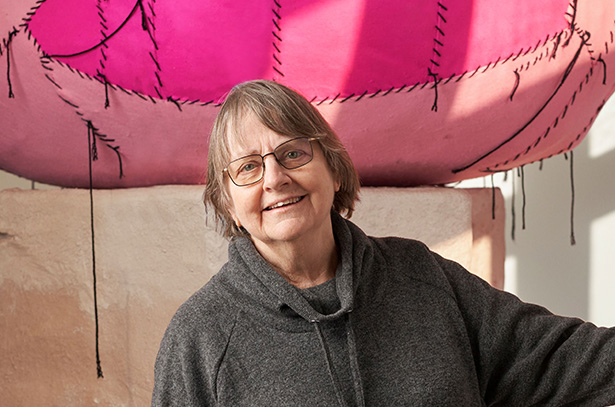

Phyllida Barlow
For almost 60 years, British artist Phyllida Barlow took inspiration from her surroundings to create imposing installations that can be at once menacing and playful. She created large-scale yet anti-monumental sculptures from inexpensive, low-grade materials such as cardboard, fabric, plywood, polystyrene, scrim, plaster and cement. These constructions were often painted in industrial or vibrant colors, the seams of their construction left at times visible, revealing the means of their making.
Barlow’s restless invented forms stretch the limits of mass, volume and height as they block, straddle and balance precariously. The audience is challenged into a new relationship with the sculptural object, the gallery environment and the world beyond.
‘There’s something about walking around sculpture that has the possibility of being reflective, like walking through a landscape,’ Barlow has said. ‘The largeness of sculpture has that infinite possibility to make one engage beyond just the object itself and into other realms of experience.’
Barlow exhibited extensively across institutions internationally and in 2017 represented Britain at the Venice Biennale.
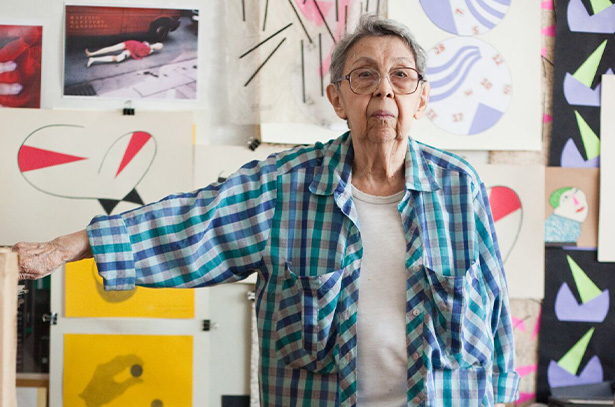

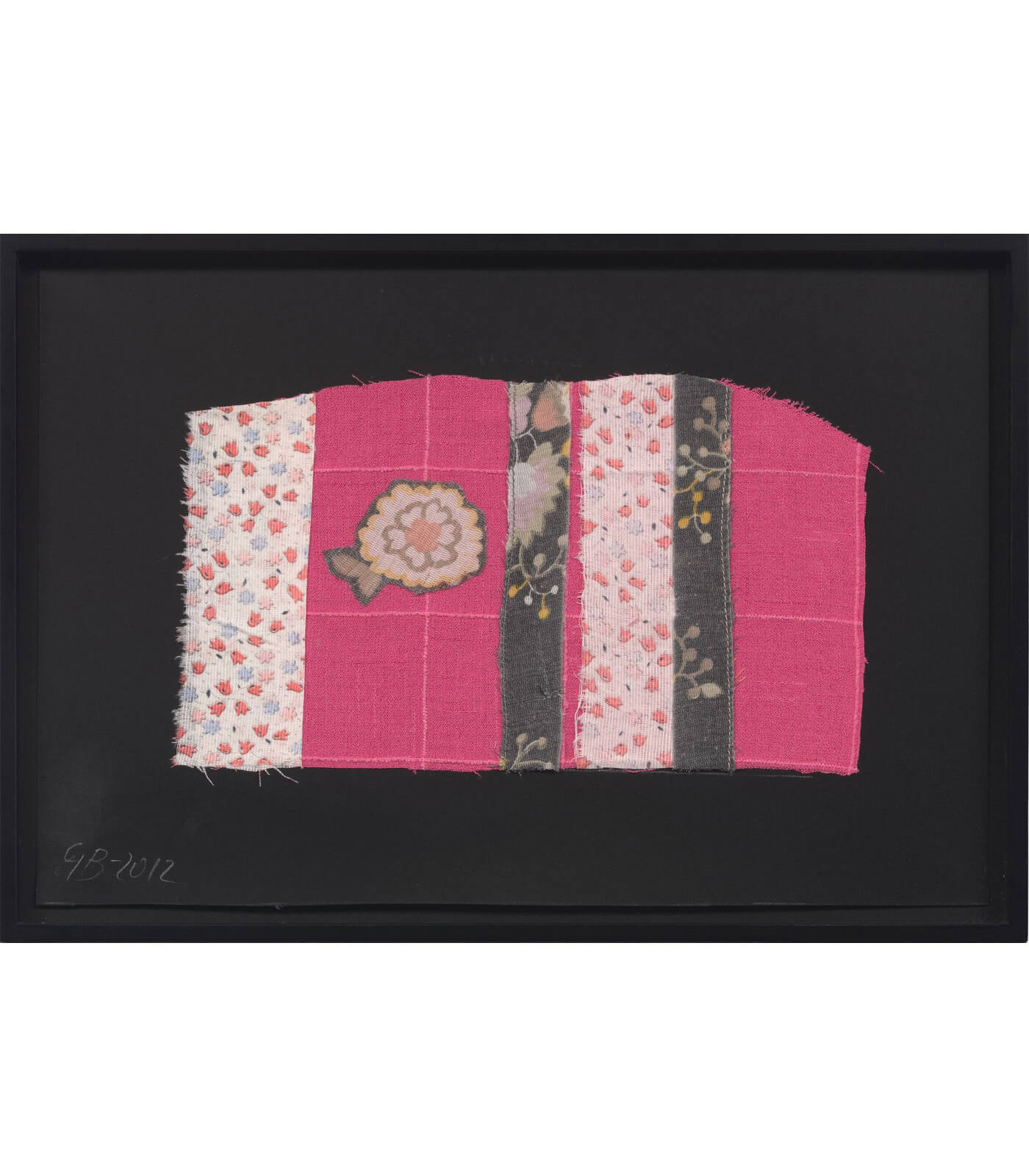
Geta Brătescu
One of the first representatives of conceptualist approaches in Romania, Geta Brătescu’s oeuvre comprises drawing, collage, textiles, photography, experimental film and performance. In her seven-decade career, she has published a number of books documenting her daily studio activities and personal experiences of art and travel.
Brătescu spent much of her working life in Bucharest under the Communist regime. She developed a deeply personal practice concerned with themes of identity, gender and dematerialisation. Her aesthetic—lo-fi, handmade, incorporating inexpensive, everyday materials—evolved from an attitude towards her studio as a safe environment of enclosure as well as a stage for playful invention. Memorialised in a key film, ‘The Studio,’ 1978 was a room of her own in which she could create work independently.
In addition to the objects and materials at hand, Brătescu was devoted to literature and would often draw inspiration from the stories of characters in famous texts. Aesop and Medea, Mother Courage and Faust, all played starring roles in her work, functioning as alter-egos and conduits for self-expression and frequently an oblique form of political subversion.
From 1945 to 1949, she studied at the Faculty of Letters and Philosophy at the University of Bucharest and at the Bucharest Academy of Fine Arts. In 1950 her studies were interrupted by the Communist government, and she was unable to complete her art education until 1971. Following her exclusion from university, Brătescu maintained a studio practice whilst working as an illustrator and graphic designer, becoming in the early 1960s the artistic director of the prestigious literary magazine, Secolul 20.
In 2008 Brătescu was honored with the title of Doctor Honoris Causa from the National Arts University in Bucharest for her contribution to the landscape of contemporary Romanian art. In 2017 she represented Romania at the Venice Biennale and was awarded by the President of Romania the Order of the Star of Romania.
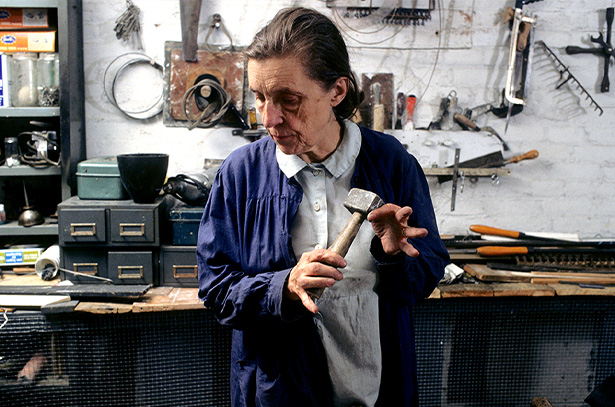

Louise Bourgeois
Born in France in 1911, and working in America from 1938 until her death in 2010, Louise Bourgeois is recognized as one of the most important and influential artists of our time. For over seven decades, Bourgeois’s creative process was fueled by an introspective reality, often rooted in cathartic re-visitations of early childhood trauma and frank examinations of female sexuality. Articulated by recurrent motifs (including body parts, houses and spiders), personal symbolism and psychological release, the conceptual and stylistic complexity of Bourgeois’s oeuvre—employing a variety of genres, media and materials—plays upon the powers of association, memory, fantasy, and fear.
Bourgeois’s work is inextricably entwined with her life and experiences: fathoming the depths of emotion and psychology across two- and three-dimensional planes of expression. ‘Art,’ as she once remarked in an interview, ‘is the experience, the re-experience of a trauma.’ Arising from distinct and highly individualized processes of conceptualization, Bourgeois's multiplicity of forms and materials enact a perpetual play: at once embedding and conjuring emotions, only to dispel and disperse their psychological grasp. Employing motifs, dramatic colors, dense skeins of thread, and vast variety of media, Bourgeois's distinctive symbolic code enmeshes the complexities of the human experience and individual introspection.
Rather than pursuing formalist concerns for their own sake, Bourgeois endeavored to find the most appropriate means of expressing her ideas and emotions, combining a wide range of materials—variously, fabric, plaster, latex, marble and bronze—with an endless repertoire of found objects. Although her oeuvre traverses the realms of painting, drawing, printmaking, and performance, Bourgeois remains best known for her work in sculpture.
Bourgeois’s early works include her distinct 'Personages' from the late 1940s and early 1950s; a series of free-standing sculptures which reference the human figure and various urban structures, including skyscrapers. The ‘Personages’ served as physical surrogates for the friends and family Bourgeois had left behind in France, while also highlighting an interest in architecture dating back to her childhood. Her installation of these sculptures as clustered ‘environments’ in 1949 and 1950 foreshadowed the immersive encounters of installation art twenty years before the genre’s rise to prominence.
Bourgeois’s work was included in the seminal exhibition ‘Eccentric Abstraction,’ curated by Lucy Lippard for New York's Fischbach Gallery in 1966. Major breakthroughs on the international scene followed with The Museum of Modern Art in New York's 1982 retrospective of her work; Bourgeois's participation in Documenta IX in 1992; and her representation of the United States at the 45th Venice Biennale in 1993.
In 2001, Bourgeois was the first artist commissioned to fill the Tate Modern’s cavernous Turbine Hall. The Tate Modern’s 2007 retrospective of her works, which subsequently traveled to the Centre Pompidou in Paris; The Guggenheim Museum in New York; The Museum of Contemporary Art in Los Angeles; and The Hirshhorn Museum & Sculpture Garden in Washington D.C., cemented her legacy as a foremost grande dame of late Modernism.
Header image: Louise Bourgeois, ARCHED FIGURE, 1993 © The Easton Foundation/VAGA, NY, Photo: Christopher Burke
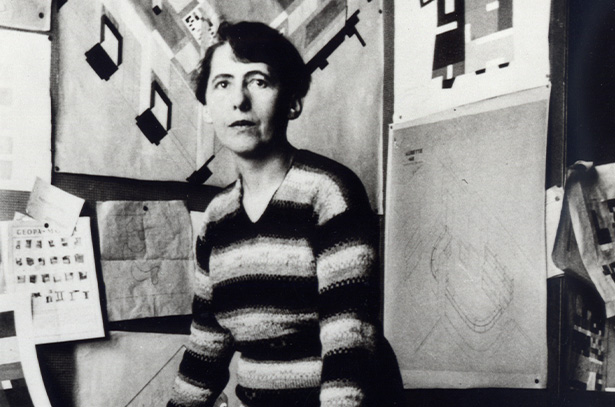

Sophie Taeuber-Arp
Sophie Taeuber-Arp (1889 – 1943) is one of the most important artists of the twentieth-century avant-garde and is considered a pioneer of Constructivist art. Reconciling extremes with confidence—Dada and Geometric Abstraction, fine art and utilitarian objects—Taeuber-Arp’s works boldly engaged with the intellectual context of international modernism. Through her multi-faceted approach to media, she challenged traditional hierarchies between fine and applied art, and asserted art’s urgent relevance to daily life. Taeuber-Arp defied categorization during her brief career through her work as a painter, sculptor, architect, performer, choreographer, teacher, writer, and designer of textiles, stage sets and interiors.
Born in Davos, Switzerland, Sophie Taeuber-Arp began her studies at the School of Applied Arts in St. Gallen between 1906 and 1910, studying textile design and embroidery. She later moved to the experimental workshops of Hermann Obrist and Wilhelm von Debschitz in Munich, where she learned a variety of techniques in fine and applied art and architecture, before spending a year studying weaving at the School of Arts and Crafts in Hamburg. The outbreak of World War I in 1914 forced Taeuber-Arp to return to Switzerland, where in 1915 she took lessons in Ausdruckstanz (expressive dance), with the choreographer Rudolf von Laban and the revolutionary dancer Mary Wigman. The same year, during a visit to the Galerie Tanner in Zurich, she met her future husband Hans Arp, whom she married in 1922.
Between 1916 and 1919, Taeuber-Arp was a key member in the Zurich Dada movement, performing in modern expressive dances at the Cabaret Voltaire and the Galerie Dada. From 1916–1929, Taeuber-Arp taught textile design at the Zurich School of Arts and Crafts. Her teaching methods in color theory and abstraction were informed by her own practice that deliberately favored mediums and techniques that challenged accepted hierarchies—whether that was through her pioneering use of the grid, free-flowing geometric forms or abstracted figures. In these years, Taeuber-Arp produced collages, watercolors, textile works and stage sets, marionettes and tapestries, utilizing a unique interplay between color and form which would later solidify her place as an early founder of Constructivist art.
1926 was a turning point in Taeuber-Arp’s career, when she was commissioned to design the interior of the Aubette, a cultural center, in Strasbourg—a project she asked Hans Arp and Theo van Doesburg to collaborate with her on. Once completed in 1928, van Doesburg devoted an issue of his journal De Stijl to their groundbreaking design of a public environment that inextricably melded art with daily life.
The Aubette commission gave Taeuber-Arp and her husband economic freedom that allowed them to move to Meudon, near Paris, where she conceived and designed their house and studio and some of its furniture. This marked the beginning of the most productive period in Taeuber-Arp’s life. She joined various artistic collectives from Cercle et Carré to Abstraction-Création and the Swiss group Allianz alongside fellow artists such as Georges Vantongerloo, Piet Mondrian and Max Bill, and founded and edited the radical art magazine Plastique. Arp’s and Taeuber-Arp’s house in Meudon became a meeting place for artists, writers and other intellectuals. Their circle of friends included the artists Sonia and Robert Delaunay, Wassily Kandinsky, Joan Miró, and Marcel Duchamp. Between 1929 and 1943, Taeuber-Arp exhibited in 40 exhibitions across the globe.
Taeuber-Arp and her husband fled to Southern France when the Nazis invaded Paris, before crossing over to Zurich in late 1942. The following year she died tragically and prematurely from accidental carbon monoxide poisoning.
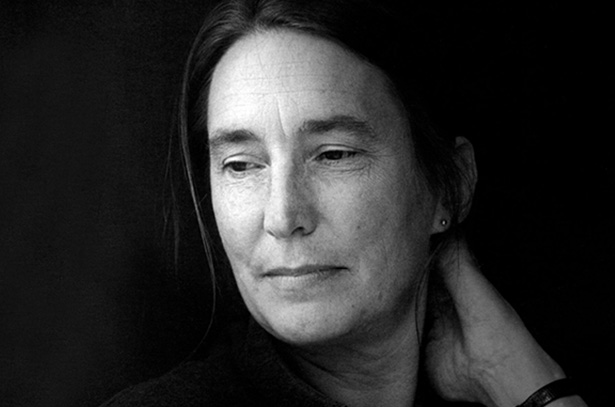

Jenny Holzer
Jenny Holzer is an American conceptual and installation artist whose work deploys text in public spaces across an array of media, including electronic signs, carved stone, paintings, billboards, and printed materials. Holzer’s oeuvre provokes public debate and illuminates social and political justice. Celebrated for her inimitable use of language and projects in the public sphere, Holzer creates a powerful tension between the realms of feeling and knowledge, with a practice that encompasses both individual and collective experiences of power and violence, vulnerability and tenderness.
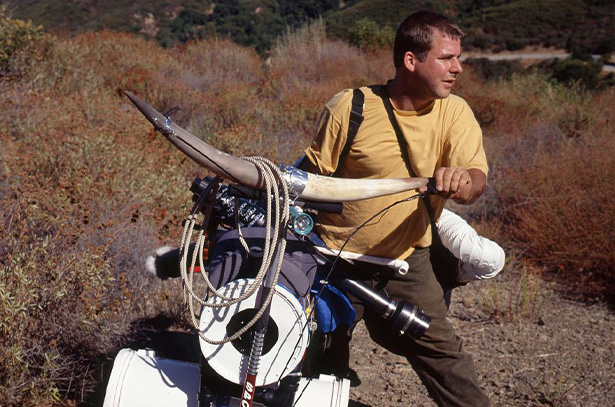

Jason Rhoades
Jason Rhoades (1965 – 2006) was a visionary artist and world builder for whom sculpture and myth were intertwined forms of construction. His epic assemblage installations established him as a force of the international art world in the 1990s, while based in Los Angeles. America was his art’s imaginative subject, which he represented with a provocative sense of irony and materialism, along with disarming humor and authentic identification.
Working on an architectural scale, Rhoades created immersive environmental sculptures that deployed copious quantities of consumer goods (Q-tips, computers, knickknacks), building supplies (plastic buckets, Sheetrock, extension cords), media (video games, hip-hop music, porn) and neon light. Imbued with a barely contained sense of chaos, these works are also highly crafted and surprisingly formal in their composition. Pattern, order, information networks, narrative threads, color and line give shape to Rhoades’ installations as diagrammatic depictions and systems of meaning. He considered art a tool for pursuing life’s big questions and dedicated major works to exploring the act of creation as signified by a garage, the brain, Brancusi’s studio and a penis, among other metaphorical sites. The car was also instrumental to Rhoades’ project as a readymade sculpture, as a conceptual space akin to the studio and as a vehicle for the driving ambition he held for his art. 'If you know my work', he said, 'you know that it is never finished'.
Inquire about available works
‘Chromophilia’ is on view now through 9 March 2022 at Hauser & Wirth Zurich, Limmatstrasse.
Related Content
Current Exhibitions
1 / 10





























